Why Should You Hack a Digital Meter?
The consumer can reduce their electricity bills by pretending to use less electricity. This may take the form of some trickeries, including meter tampering, using hidden connections (bypassing meter connections), physical destruction of energy meters, stopping the rotation of energy meters’ disks, and storing units by the meter reader. Digital meter hacks occur in most regions of the world where utility bills run up. It is done in different ways, but the most efficient of which is done by using a Meter Hack Device. In this article, we are going to investigate how to hack digital meter.
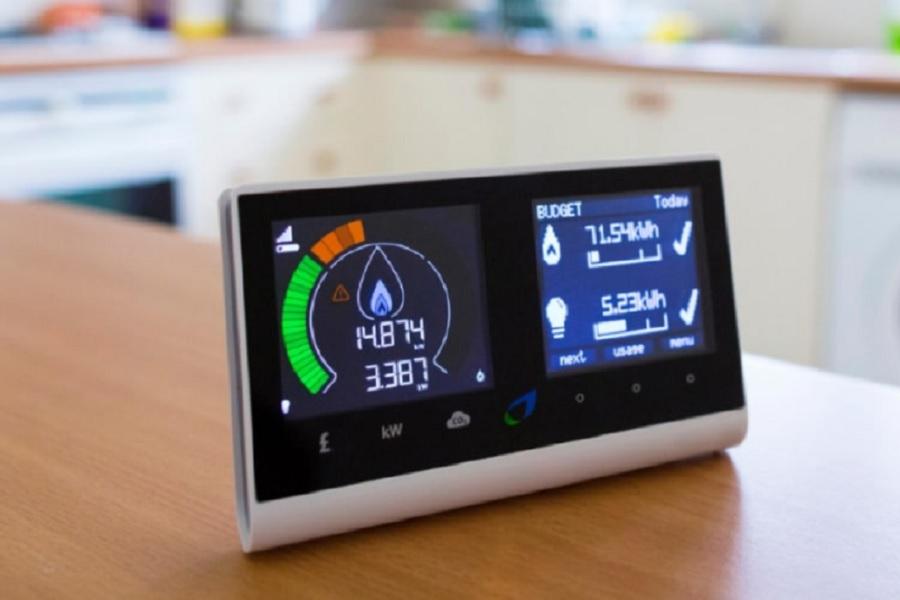

What Is a Digital Meter?
A digital, or a smart, meter is a digital device that collects electricity usage data and sends it to a local utility through a telecommunications connection. The meters can be used to remotely turn off customers’ power, for example in the case of unpaid bills, as well as to help customers learn more about how much electricity they are using.
Like circuit breakers in a household panel, power grid components can “trip” and shut down when demand, or load, is too high or problematic for some other reason. As a result, the load is transferred to other grid network nodes, which may also shut down, raising the possibility of a chain reaction that could result in a blackout.
Hackers can control smart meter switches to cause load oscillations by breaking into the advanced metering infrastructure, also known as AMI. This is one of the attack types made possible by the new technologies.
Is it Possible to Hack a Digital Meter?
Any computer (or processor) can be ‘hacked’. Another query is whether it can be done unnoticed. Often the process of attempting to ‘hack’ involves many trials (each of which can be a separate offense under most computer crime laws). Many smart meters have multiple layers of protection, beginning with the possibility of using unique protocols and operating systems. Similar to cable TV boxes, the expense of cracking into the system is greater than the expense of the service, making the cost of creating a hack higher than the potential return.
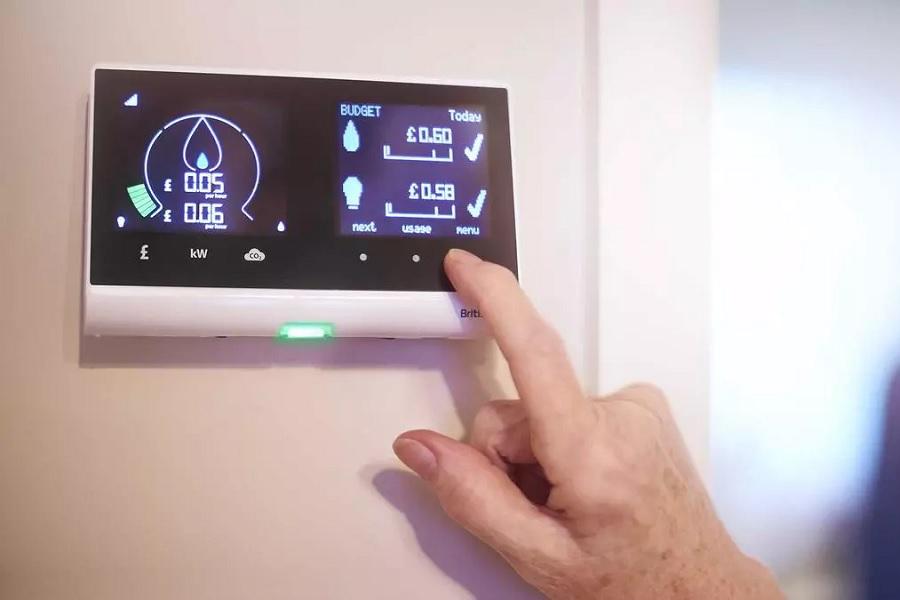

It is possible for smart meters to be hacked, just like any other computerized device connected to a network. Smart meters use wireless technology to communicate with the utility company, and if the network is not properly secured, it could potentially be accessed by unauthorized parties. Additionally, if the smart meter itself is not properly configured or has a software vulnerability, it could also be susceptible to hacking.
What Is Meant by Hacking a Digital Meter
These days, utility bills usually run up, especially in countries where electricity, water, and gas are expensive for home and industrial users. So, one way to reduce the utility bill is to hack a digital meter so that it will show less consumption. There are various ways to do this, but we will mention the most effective method in the following.
Although it may not seem like it, the electrical meter on the side of your house is quite technologically advanced. Now a node on a vast network, what was once a straightforward electromechanical device that a person would have to read in person.
Your meter not only calculates how much electricity you use, but it also communicates with other meters nearby, sending data skipping across town to routers that you might have never noticed as it returns to the utility. And the most advanced smart meters can deduce which appliances are being used simply by observing usage patterns. They do this by tracking patterns of usage in addition to tracking how much electricity you are using.

Having a network of wirelessly communicating smart meters may sound great for utility companies, but what does it mean for the customers? Are these devices vulnerable to attack? If something is intended to be used for 15 years or more, have they been engineered to be as hard to exploit as they should be?
In this type of electricity theft, the victim connects a cable directly to the nearby LT line or pole without using a legitimate electrical connection. The individual who commits the theft in this instance takes the entire unit. This type of electrical theft technique is also known as a “Katia connection”. In the following, we will mention various ways to manipulate a digital meter.
Meter bypass
When a meter is bypassed, the consumer will illegally consume power (kWh) or electrical energy (kWh) through an additional cable by cutting the service cable before the meter. Meaning that the consumer cuts the main cable before the meter and then uses the second cable to steal power from the cable that runs from the closest pole to the meter.
In this scenario, some energy passes through the meter, whose bill will be paid by the customer via the bill. The power theft, however, will include the energy that passes through the cable before the energy meter. Meaning that half of the energy will be stolen and half of the bill will be paid by the customer.
Can a Digital Meter Detect a Bypass?
Yes, but not immediately. The electric utility may become aware and show up to investigate if someone tampers with an electric meter (smart meter or otherwise) and it reads zero for several months.

The electric utility will be alerted right away if the smart meter is completely disconnected (i.e., not powered on), as a power outage at that address will indicate the number of times per hour smart meters communicate via radio.
In one incident, a household’s non-smart electric meter stopped working completely. After two months of zero usage electric bills, the husband called the electric company and told them that the electric meter wasn’t working. The interesting thing is that the electric utility did nothing. Two months later and with two more zero-usage bills, the husband again called them to tell them that the meter wasn’t working. Then again, the electric utility did nothing.
Meter tampering
It has come to light that smart meters are not immune to tampering, which can allow malicious actors to bypass security measures. To achieve this, the attacker would need to physically access the meter and manipulate either the software or hardware components. One such method involves slowing down the meter by adding a device or resistance in parallel or series across the C T. As a result of this manipulation, the consumer would only be charged for a portion of the units that have been measured by the meter, while the remaining units go unrecorded due to the added resistance. This can potentially lead to a lower bill for the consumer in cases of theft.
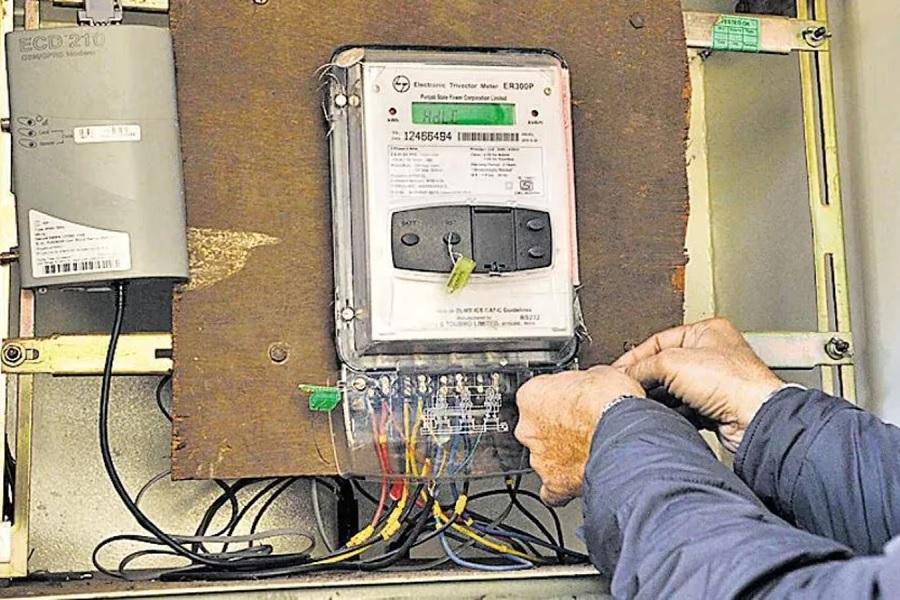
Readings storing (kWh)
If a consumer’s meter displays a reading that is lower than their actual consumption, they may receive a bill for the lower amount from a meter reader. It is important to note, however, that if the meter displays an unusually high reading, the meter may have been tampered with and replaced illegally. As an illustration, we can consider the case of a consumer’s usage:
- Jan 20: 100 units
- Feb 20: 200 units
According to the records, the energy consumption for February 2020 was expected to be 200 units. However, the reader only posted 150 units for that particular month. As a result, the remaining 50 units will be kept in storage and gradually posted in the following months until it has been fully accounted for. This will result in a larger accumulation of kWh readings being stored for future reference.
At some point, the meter will need to be replaced due to apparent damage. When this happens, any stored readings will need to be eliminated as the new meter is installed. Once the new meter is in place, a new bill will be created based on the updated readings. This process ensures that accurate and up-to-date information is provided to the customer, helping them to manage their energy consumption more effectively.
Meter Damaging
This type of tampering is done to electromechanical type meters with a rotating element. Foreign material (device) is placed inside the meter to obstruct the free movement of the disc. A slower rotating disk signals less energy consumption.

Digital meters are widely used in the modern world due to their advanced and smart features. However, they are not immune to vulnerabilities, particularly hacking. Over the years, hackers have been able to manipulate these meters successfully, which is a cause for concern. Thus, it is imperative to understand the various methods used to manipulate digital meters to prevent such occurrences. In this article, we will delve deeper into the subject and provide detailed insights into the various ways in which digital meters can be manipulated.
If a meter is damaged, an IDF-based bill will be issued. This means that the bill will be calculated based on the average unit usage over the past few months. Some consumers intentionally damage their meters and request that the meter reader generate lower unit bills for three consecutive months. This is done to lower the average unit usage and ultimately result in a lower IDF-based bill.
Let’s say there were three bills: 50 units on January 20th, 40 units on February 20th, and 30 units on March. The IDF bill will be an average of 40 units. Even if the consumer spends 100 to 200 per unit per month, their bill on IDF will only be for 40 units.
Please note that electricity theft is a punishable act and can be detected easily. If you want to reduce your utility bills, there are more advanced ways hacking digital meters, like using a jammer device. An electrical grid can be destabilized by hackers who manipulate smart meters to create an oscillation in electricity demand.

Replay attacks
In the event of a replay attack, which is a type of cyber attack, a malevolent individual can intercept the data that is being transmitted from the smart meter to the utility company. Once they have access to the data, they can replay the same information to show that less energy was consumed than it was. This could result in the customer being charged less for their energy usage than they should be, potentially leading to financial loss for the utility company and an unfair advantage for the customer. Therefore, it is crucial to have measures in place to prevent such attacks and ensure the accuracy of energy usage data.
Remote hacking
When a smart meter is linked to an insecure network, it could potentially be vulnerable to remote hacking. This means that an attacker could exploit either a weakness in the software or the network itself to gain access to the meter and manipulate its readings. This could have serious consequences, such as inaccurate billing or even a potential safety hazard if the readings relate to energy consumption or usage. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that any smart meter is connected to a secure network to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Denial of service attacks
A denial-of-service attack occurs when an overwhelming amount of requests are sent to the smart meter, causing it to malfunction. This malfunction can lead to issues such as the inability to send data to the utility company, resulting in problems with billing and other related matters. It is a serious concern that requires immediate attention to prevent the potential damage it can cause.

Side-channel attacks
Side-channel attacks are a form of security breach in which confidential data is obtained by analyzing the physical characteristics of a device. This technique involves observing the energy consumption of a smart meter, for example, to detect when a user is utilizing energy-intensive appliances such as a washing machine or air conditioner. By doing so, attackers can potentially infer when the user is not present at home, exposing them to further breaches and security risks.
Malware Attack
It has been discovered that smart meters, which are designed to measure and record energy usage in homes and businesses, are vulnerable to malware infection. This is a major concern because once a smart meter becomes infected with malware, unauthorized parties can gain access to the device and manipulate the readings.
Specifically, malware can alter the firmware of the smart meter, which then provides remote control access to an attacker. This can result in significant consequences, such as inaccurate billing or even a complete takeover of the device.
What Is the Best Way to Hack a Digital Meter?
The best and the safest way to hack a digital meter is by a jammer. A jammer is a device that uses radio waves to interrupt the digital meter’s record, so that you will receive utility bills with less amounts to pay. Jammers also are safe to work with and will have no dangers. These devices are also cost-effective.

Full Jammer Provides You with the Best Solution to Reduce Your Utility Bills
As was explained, it is possible to hack a digital meter. The most effective way to hack a digital meter is by using a jammer device which is also easy to use. Full Jammer is a leading producer of jammers to help you reduce your utility bills. You can select your product from a variety of jammers and make the payment through cryptocurrencies which are untraceable. Also, you will receive your device on time and under other names, so no one will suspect what is inside the package.



Recent Comments